Measurement
Grades 5-7
|
Ohio Benchmarks
Grades 5-7
|
Grade-Level Indicators
Grade 5
|
Grade-Level Indicators
Grade 6
|
Grade-Level Indicators
Grade 7
|
|
A.
Select appropriate units to measure angles,
circumference, surface area, mass and volume, using:
·
U.S. customary units; e.g., degrees, square feet, pounds, and other
units as appropriate;
·
Metric units; e.g., square meters, kilograms and other units as
appropriate.
|
1.
Identify and select
appropriate units to measure angles; i.e.,
degrees.
|
|
1.
Select appropriate units
for measuring derived measurements; e.g., miles per hour, revolutions
per minute.
|
|
B.
Convert units of length,
area, volume, mass and time within the same measurement system.
|
5.
Make simple unit conversions within a measurement system;
e.g., inches to feet, kilograms to grams, quarts to gallons.(Grade
4)
5.
Make conversions within the same measurement system while performing
computations.
|
|
2.
Convert units of area
and volume within the same measurement system using proportional
reasoning and a reference table when appropriate; e.g., square feet to
square yards, cubic meters to cubic centimeters.
|
Measurement
Grades 5-7
|
Ohio Benchmarks
Grades 5-7
|
Grade-Level Indicators
Grade 5
|
Grade-Level Indicators
Grade 6
|
Grade-Level Indicators
Grade 7
|
|
C.
Identify appropriate
tools and apply appropriate techniques for measuring angles, perimeter
or circumference and area of triangles, quadrilaterals, circles, and
composite shapes, and surface area and
volume of prisms and cylinders.
|
6.
Use strategies to develop formulas for determining perimeter and area
of triangles, rectangles and parallelograms, and volume of rectangular
prisms.
7.
Use benchmark angles (e.g.; 45º, 90º, 120º) to
estimate the measure of angles, and use a tool to measure and draw
angles.
|
2.
Use strategies to develop formulas for finding circumference and area
of circles, and to determine the area of sectors; e.g., 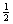 circle, circle, 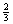 circle, circle, 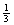 circle, circle, 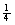 circle. circle.
3.
Estimate perimeter or circumference and area for circles, triangles and
quadrilaterals, and surface area and volume for prisms and cylinders by:
a.
estimating lengths using
string or links, areas using tiles or
grid, and volumes using cubes;
b.
measuring attributes
(diameter, side lengths, or heights) and using established formulas for
circles, triangles, rectangles, parallelograms and rectangular prisms.
|
6. Use strategies
to develop formulas for finding area of trapezoids and volume of
cylinders and prisms.
7. Develop
strategies to find the area of composite shapes using the areas of
triangles, parallelograms, circles and sectors.
|
Measurement
Grades 5-7
|
Ohio Benchmarks
Grades 5-7
|
Grade-Level Indicators
Grade 5
|
Grade-Level Indicators
Grade 6
|
Grade-Level Indicators
Grade 7
|
| |
|
Note: There are instances when a grade-level indicator for
one
standard is linked to a benchmark for a different standard.
See also correlation for Patterns, Functions and Algebra
for indicator 2.
|
Note: There are instances when a grade-level indicator for
one
standard is linked to a benchmark for a different standard.
See also correlation for Patterns, Functions and Algebra
for indicator 6.
|
|
D.
Select a tool and
measure accurately to a specified level of precision.
|
|
|
3.
Estimate a measurement
to a greater degree of precision than the tool provides.
|
|
E.
Use problem solving
techniques and technology as needed to solve problems involving length,
weight, perimeter, area, volume, time and temperature.
|
6.
Write, solve and verify solutions to multi-step problems
involving measurement. (Grade 4)
2.
Identify paths between
points on a grid or coordinate plane and compare the lengths of the
paths; e.g., shortest path, paths of equal
length.
|
4.
Determine which measure (perimeter, area, surface area, volume) matches
the context for a problem situation; e.g., perimeter is the context
for fencing a garden, surface area is the context for painting a
room.
|
4.
Solve problems involving proportional relationships and scale factors;
e.g., scale models that require unit conversions within the same
measurement system.
|
Measurement
Grades 5-7
|
Ohio Benchmarks
Grades 5-7
|
Grade-Level Indicators
Grade 5
|
Grade-Level Indicators
Grade 6
|
Grade-Level Indicators
Grade 7
|
|
F.
Analyze and explain what
happens to area and perimeter or surface area and volume when the
dimensions of an object are changed.
|
3.
Demonstrate and describe
the differences between covering the faces (surface area) and filling
the interior (volume) of three-dimensional objects.
4.
Demonstrate
understanding of the differences among linear units, square units and
cubic units.
|
1.
Understand and describe
the difference between surface area and volume.
6.
Describe what happens to the perimeter and area of a two-dimensional
shape when the measurements of the shape are changed; e.g. length of
sides are doubled.
|
|
